
Use of Eco-Friendly Materials in The Future of Construction
Urbanization is the goal of any country hence it appears that concrete, steel, aluminium, and plastic seem like they are here to stay. However, the new trends in construction may choose to differ since they are swaying towards using more eco-friendly materials in building design, in an attempt to reduce their carbon footprint on the environment.
What is eco-friendly construction?
An eco-friendly construction may use eco-friendly materials or deploy eco-friendly techniques that are non-harmful to the environment and provide natural comfort to the users. This type of construction also emphasizes on using local and renewable materials therefore reducing the use of concrete.
Bamboo, for example, is eco-friendly and has many applications in modern-day construction. On the other hand, depending on the construction technique used, even conventional materials can contribute to constructing environment-friendly buildings. For example, rat trap bond is a brick masonry method of wall construction that uses fewer bricks and is more heat-insulating than standard walls and therefore eco-friendly.
Another definition of eco-friendly construction highlights using materials that have high embodied energy as high energy is required for producing them. For example, steel and aluminium require high energy compared to timber.
The below picture underlines the various properties of eco-friendly materials.
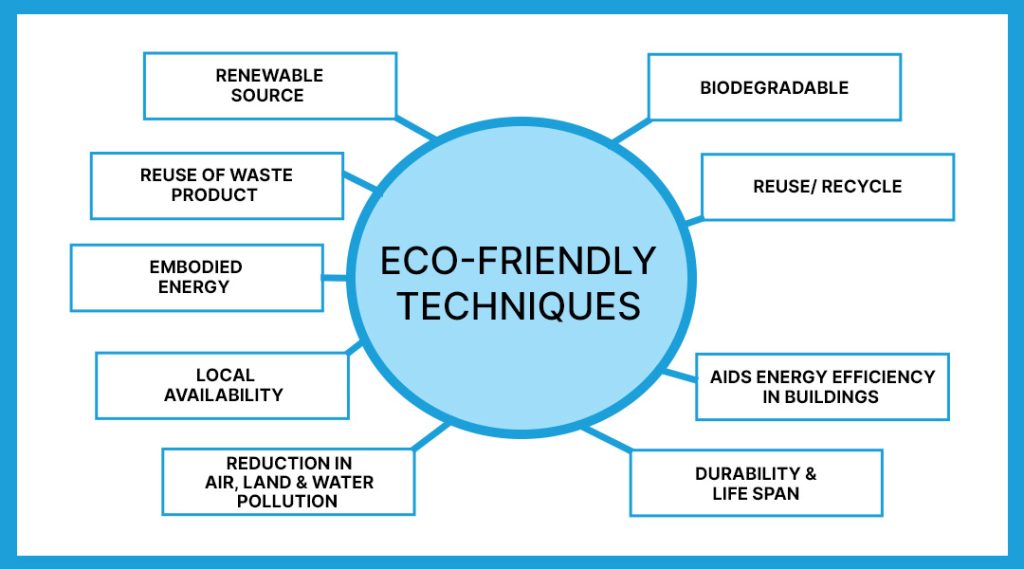
But the question that comes to mind is whether eco-friendly constructions will be strong and durable.
Reinforced concrete has become a symbol of strength and toughness in building construction and is thus used in abundance in construction projects. Sadly, this principle construction component is also the principal producer of GHG emissions which causes significant environmental danger.
Governments have therefore begun to promote the use of traditional and environmentally-friendly materials in construction as much as possible. They are also encouraging research to identify eco-friendly building materials and improve their mechanical performances and water-resistant characteristics.
However, despite the significance of this research, the jury is out that the eco-friendly materials cannot match the mechanical performance, rate of construction, and economic efficiency offered by the RCC.
The solution lies in the Hybrid model
The hybrid model combines the benefits of reinforced concrete with the benefits of sustainable construction materials so that the structure gets mechanical performance and economic efficiency along with improved ecological and bioclimatic characteristics. Efforts should also be made to lessen the polluting effects of RCC and improve its sustainability.
The Importance of Sustainable Building Practices
Eco-friendly constructions are more than just a passing trend; they represent a fundamental shift towards a more sustainable future. Traditional construction methods have relied heavily on non-renewable resources and have contributed to significant carbon emissions. In contrast, sustainable building practices prioritize energy efficiency, reduced waste, and the use of environmentally friendly materials. By embracing these practices, we can significantly reduce our ecological footprint and mitigate the negative impact of construction on the environment.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Constructions
The benefits of eco-friendly constructions extend beyond environmental considerations. These buildings offer numerous advantages for both occupants and the community at large.
Certainly, here are the benefits of eco-friendly constructions presented as bullet points:
Improved Indoor Air Quality: Incorporates natural ventilation and low-toxicity materials, leading to better air quality and enhanced health outcomes, especially for those with respiratory issues.
Energy Efficiency: Designed for energy efficiency, leading to lower utility costs for occupants and reduced strain on infrastructure and resources.
Savings: Reduced utility costs result in financial savings for occupants over time, making eco-friendly buildings cost-effective in the long run.
Environmental Impact: Minimizes the carbon footprint and resource consumption, contributing to overall ecological preservation and sustainability.
Community Health: Enhances the overall well-being of the community by reducing pollution and promoting a healthier living environment.
Job Creation: Utilization of sustainable materials creates job opportunities in the renewable resources sector, stimulating local economies.
Innovation and Technology: Drives innovation in construction practices and encourages the development of advanced technologies for sustainable building solutions.
Long-Term Investment: Offers long-term benefits with increased property value and lower maintenance costs, making it a prudent investment choice.
Resilience: Often designed to withstand natural disasters better, increasing the resilience of both the building and the community.
Education and Awareness: Raises awareness about sustainable living and encourages the adoption of eco-friendly practices among occupants and the larger community.
Key Features of Eco-Friendly Buildings
Eco-friendly constructions are characterized by several key features that set them apart from conventional buildings. Firstly, these buildings are designed with a focus on energy efficiency. This includes the use of energy-saving appliances, advanced insulation techniques, and the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels. Secondly, eco-friendly constructions prioritize water conservation through the implementation of rainwater harvesting systems, low-flow fixtures, and water-efficient landscaping. Additionally, these buildings often incorporate sustainable materials such as recycled steel, bamboo, and reclaimed wood, reducing the demand for virgin resources. Finally, eco-friendly constructions emphasize the importance of waste management by implementing strategies such as recycling programs and the use of recycled materials in the construction process.
What are some examples of eco-friendly and sustainable construction materials?
As said earlier, eco-friendly materials are not necessarily naturally available items. Some of the conventional building materials can also be used to develop environment-friendly construction and designs, using special techniques. The list below includes a variety of them.
Conventional Eco-friendly construction materials
These geosourced (earth, stone, and lime) and biosourced (wood and natural fibers) materials are environmentally friendly (ecological, good thermal insulation, good hygrometric regulation, fire resistance, 100% recyclable, and competitive).
- Bamboo, bamboo-based particle board & ply board, bamboo matting
- Sun-dried bricks
- Precast cement concrete blocks, lintels, and slabs. Structural and non-structural modular elements
- Calcined phosphogypsum wall panels
- Calcium silicate boards and tiles
- Cellular lightweight concrete blocks
- Cement paint
- Clay roofing tiles
- Water, polyurethane, and acrylic-based chemical admixtures for corrosion removal, rust prevention, and waterproofing
- Epoxy resin system, flooring, sealants, adhesives, and admixtures
- Ferro-cement boards for door and window shutters
- Ferro-cement roofing channels
- Fly-ash sand lime bricks and paver blocks
- Gypsum board, tiles, plaster, blocks, gypsum plaster fiber jute/sisal, and glass fiber composites
- Laminated wood plastic components
- Marble mosaic tiles
- MDF boards and moldings
- Micro concrete roofing tiles
- Particle boards
- Polymerized waterproof compound
- Portland pozzolana cement fly-ash / calcined clay based
- Portland slag cement
- RCC door frames
- Ready mix cement concrete
- Rubber wood finger joint board
- Stone dust
- Waterproof compound, adhesive, polymer, powder
Potential Eco-friendly materials & techniques
- Bagasse board
- Bricks from coal washery reject
- Building blocks from mine waste
- Burnt clay fly ash bricks
- Coir cement board
- Compressed earth blocks
- Eps composites and door shutters
- Fibre fly ash cement boards
- Fiber-reinforced concrete precast elements, wall panels, blocks, and manhole covers
- Fibrous gypsum plasterboards
- Fly ash cellular concrete, fly ash cement brick, and blocks
- Fly ash lime cellular concrete
- Fly ash lime gypsum brick
- Insulating bricks from rice husk ash
- Jute fiber polyester
- Non-erodible mud plaster
- Polytiles
- Timber from trees such as poplar, rubber, and eucalyptus
- Precast walling roofing components
- Prefab brick panel system
