How to Get Green Building Certification in India
How to Get Green Building Certification in India : Best Tips
Construction is the engine of economic growth and tops the priorities of a fast-developing nation like India, but construction is a leading source of GHG emissions too. India is facing this dilemma by encouraging sustainable development through green building certification. This blog deals with the whys and hows of green building certification in India.
What is the Concept of Green Building?
By definition and concept, a green building uses mostly locally available and natural materials, is designed for optimized energy efficiency, and uses less water during construction.
A green building design focuses on the least carbon emissions and natural comfort for the inhabitants. Therefore, it emphasizes cutting down both operational emissions and embodied emissions, using renewable energy, and reducing non-biodegradable waste, apart from other measures.
It’s worth noting that any building can be upgraded to a green building by adding or installing some criteria or features of green buildings, or by renovating to comply with the green building standard, which features:
- Adequate natural air and light for the residents
- In-built source of renewable energy
- Optimized energy efficiency
- Optimized water conservation
- Extensive use of sustainable building materials
- Efficient waste management
- Landscape
What is the Green Building Certification?
Green building certification is a methodology for evaluating and rating a building’s environmental and sustainability performance. This urges construction companies to strive to minimize the carbon footprint of their building & infrastructure projects by planning and developing in accordance with the United Nations’ sustainable development goals.
What is the Green Building Rating System?
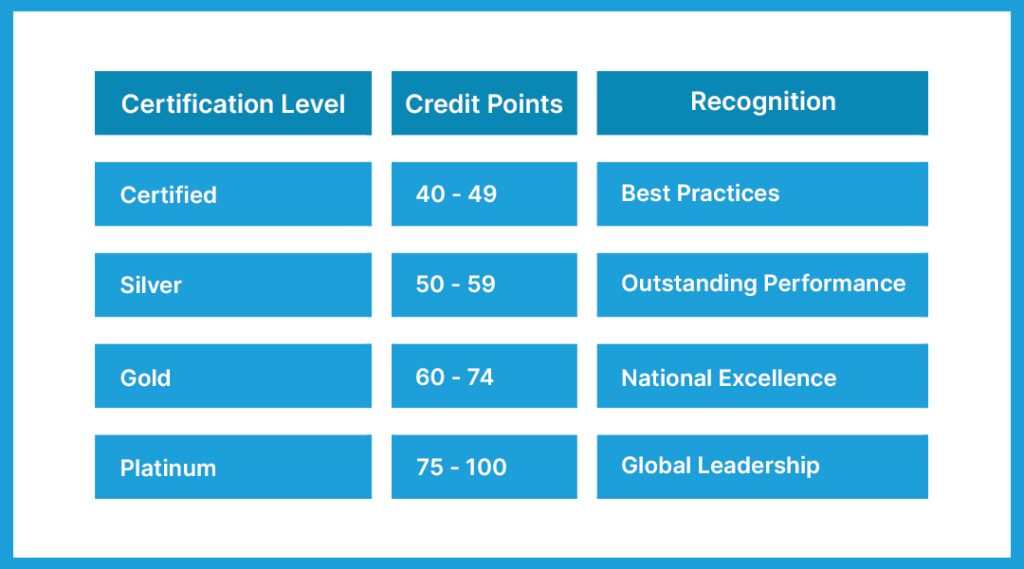
The following table explains the various categories of the certification levels with the corresponding credit points and the recognition levels applicable for new buildings, practiced by a leading rating agency, IGBC.
IGBC will provide mountable plaques and an official letter of certification to Green New Buildings that reach one of the grading levels.
What are the various Green Building Certifications in India?
Various certifications are available to confirm and encourage green building construction practices. There are currently four agencies in India to evaluate and certify green buildings. They are:
- Indian Green Building Council (IGBC),
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED),
- Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA).
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC)
IGBC
The IGBC rating system is controlled by the Indian Green Building Council, which is a part of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII). Buildings are assigned one of four ratings: certified, silver, gold, or platinum.
Depending on the nature of the project, there can be nine different sorts of certifications. These include certifications for new and existing buildings, schools, factories, houses, townships, Special Economic Zones (SEZ), landscapes, and metro systems.
LEED
LEED gives project evaluation scores based on many criteria such as water usage, energy conservation, and reliance on sustainable materials. These scores are then used to determine the ranking, which is classified as certified (40-49 points), silver (50-59 points), gold (60-79 points), and platinum (80+ points). A platinum rating is the highest possible for a structure.
According to sources, India has approximately 1,600 LEED-certified buildings, including some of the country’s most prestigious government structures.
GRIHA
The GRIHA rating system was created by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) in India, and is supported by the Indian government’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Five stars represent the highest rating according to the star system used by GRIHA. Each star is given a certain number of points, such as one star for 25 to 40 points, two stars for 41 to 55 points, three stars for 56 to 70 points, four stars for 71 to 85 points, and five stars for points of 85 and higher.
Examples of GRIHA-rated constructions are Manipal University Campus (Jaipur), Indira Paryavaran Bhawan (New Delhi), and Hotel Grand Chola (Chennai).
What are the benefits of Green Building Certifications in India?
ECBC
ECBC specifies energy performance standards for different building components in accordance with the climatic zone. This version of ECBC, launched by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency in 2017, is futuristic, programmatic, and easy to use. ECBC has its own ratings, such as ECBC, ECBC Plus, and Super ECBC.
Implementation partners are: CPWD, SDAs, State PWDs, UDD.
Benefits of Green Building Certifications in India
Green building certification entails grading and certifying a building based on a variety of criteria. These certifications and gradings give a project credibility and validate its pro-environment claims. These certificates offer useful tools to research and compare the environmental impact of the buildings for buyers or investors wishing to invest in sustainable developments.
How to Get Green Building Certification in India?
In IGBC,the procedure to get green building certification has just two steps: Registration and submission of documents.
Registration
You must register with IGBC in order to choose the IGBC Project Certification option.
The first step in getting your building IGBC certified is to register. Following that, you’ll get access to the necessary files, templates, vital communications, and other information needed for registration. Once you’ve enrolled, you can start calculations and gather documents, mandatory for submission for credits.
Required Documents for Certification
The following documents must be submitted during the preliminary and submission stages:
1) Form to be filled
2) A description of the project along with any necessary supporting documentation, such as test reports on materials, computations, declarations, contract documents, purchase invoices, manufacturer sheets, letters, etc., for each credit.
The project documentation submission has two phases:
Preliminary Phase:
All documentation must be submitted in the preliminary phase. A third-party assessor will later analyze the submitted documents and provide the report within 30 days.
Final Phase:
Clarification on the report from the third-party assessor to be submitted in this phase, which will go for the final review. Report of the final review will take another 30 days.